Iowa Neurology & Sleep, PLC
Convenient, Quality Neurological Care
Our clinic has provided expert, compassionate care for patients throughout Southeast Iowa and West-Central Illinois for 32 years. We are dedicated to medical excellence and to improving the quality of life for every patient we serve. We believe care should be simple, supportive, and patient-centered, which is why we offer both in-person and telehealth services to ensure accessible, comprehensive treatment.
Our SErvices
Simple, Supportive Healthcare
Our care team offers services to diagnose and treat a variety of conditions and provides specialized clinics in EMG, Neurology, Headache, Sleep, and Memory.
Our Providers
Here To Serve You
Our experienced physicians and advanced practice providers dedicated to delivering high-quality neurological care. Together, they bring decades of expertise in diagnosing and treating a wide range of conditions, from common headaches and sleep disorders to complex neurological diseases.
Insurance
We Accept All Major Insurance Plans
Our clinic accepts most major health insurance plans and providers to ensure you get quality care at a cost that fits your budget.
No insurance? No problem. We accept payments, and our prices are affordable.







FAQ's
Common Questions
We do not take walk ins as a referral is needed. You may use our website to email information and or call our office.
Please bring your insurance card and photo identification.
We do accept most major insurance plans, you will be expected to pay for any co-pay or deductible at the time of service as determined by your insurance company.
A neurologist specializes in diagnosing and treating disorders of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and muscles. Common conditions include headaches and migraines, stroke, seizures, neuropathy, Parkinson’s disease, Multiple Sclerosis, memory loss, dizziness, and muscle weakness. Neurologists also evaluate symptoms such as numbness, tingling, balance problems, tremors, or changes in thinking and coordination to determine the underlying cause and create a personalized treatment plan.
During a neurological exam, the neurologist evaluates how well your brain, nerves, and muscles are functioning. The exam may include comprehensive history then testing of strength, sensation, reflexes, coordination, balance, vision, speech, and memory. Your neurologist will also review your medical history and symptoms to help identify which parts of the nervous system may be affected. The exam is noninvasive, usually takes about 20–40 minutes, and helps guide any further testing or treatment that may be needed.
A headache is pain or pressure felt anywhere in the head or neck and can have many causes, such as tension, stress, dehydration, or sinus problems. A migraine is a specific type of headache caused by changes in brain activity and blood flow. Migraines are often moderate to severe, may throb on one side of the head, and are commonly accompanied by nausea, sensitivity to light or sound, and visual changes (aura).
Dementia is a general term for a group of symptoms that affect memory, thinking, and daily functioning. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia and is a specific progressive brain disorder that damages brain cells over time. In short, dementia describes the symptoms, while Alzheimer’s is one of the diseases that can cause those symptoms. Other causes of dementia can include vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal dementia.
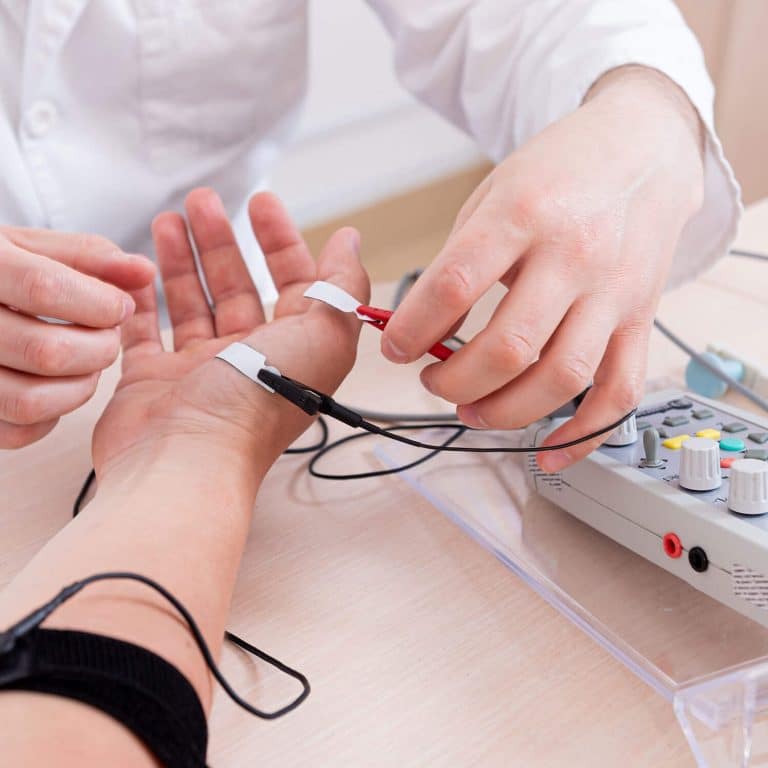
An electromyography (EMG) is a test that evaluates the health of your muscles and the nerves that control them. It helps diagnose conditions such as peripheral neuropathy, carpal tunnel syndrome, radiculopathy (pinched nerves), myopathy, and ALS and other motor neuron disorders. During the test, a small needle electrode is inserted into selected muscles to record electrical activity, and sometimes nerve conduction studies (NCS) are performed to measure how well signals travel along your nerves. Patients generally describe the test as mildly uncomfortable but not painful.
Avoid caffeine the day of the test and do not apply lotions or oils on your arms or legs.
Wear loose, comfortable clothing so the tested areas are easily accessible. Continue your usual medications unless your neurologist instructs otherwise.
A stroke occurs when blood flow to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting enough oxygen and nutrients. This can cause brain cells to die and may lead to lasting neurological problems.
There are two main types of stroke:
- Ischemic stroke: Caused by a blood clot blocking a blood vessel in the brain.
- Hemorrhagic stroke: Caused by bleeding in or around the brain.
Symptoms can include: sudden weakness or numbness, trouble speaking, vision changes, loss of balance, or a severe headache. Immediate medical attention is critical, as early treatment can save brain function and improve recovery.
The best way to determine whether someone is having a stroke or not is to think FAST:
- Face: Ask the person to smile — does the face look uneven?
- Arms: Ask the person to raise both arms — does one arm drift down?
- Speech: Ask the person to repeat a simple phrase — does their speech sound strange?
- Time: If you observe any of these signs, call 911 immediately.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic neurological disease in which the body’s immune system attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers (myelin) in the brain and spinal cord. This disrupts communication between the brain and the rest of the body, leading to a wide range of symptoms such as weakness, numbness, vision problems, balance difficulties, fatigue, and cognitive changes. MS can vary greatly from person to person, and while there is no cure, early diagnosis and personalized treatment can help slow disease progression, manage symptoms, and improve quality of life.
A sleep study evaluates your sleep patterns and helps diagnose sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, insomnia, restless legs, and narcolepsy. There are different types of studies:
- Polysomnography (PSG): Conducted overnight in a sleep lab, PSG monitors brain activity, eye movements, heart rate, breathing, oxygen levels, and muscle activity. It provides the most detailed information about your sleep.
- Home Sleep Test (HST): Performed at home, WatchPAT: A wearable device that tracks oxygen, pulse, sleep stages, and respiratory patterns at home. It is simple, noninvasive, and provides accurate results for diagnosing sleep apnea.
Avoid caffeine or alcohol for at least 6–8 hours before the test. Take usual medications unless your doctor instructs otherwise. Wear comfortable sleepwear and plan to use your usual bedtime routine items. Begin rested and follow instructions provided by the sleep lab or device kit.